5 Tips for Calculating Car Finance Rates
Understanding the complexities of car finance rates is crucial whether you're looking to lease or purchase a vehicle. This post will guide you through five essential tips that can help you secure the best possible rate for your car financing, ensuring you make an informed decision on one of life's major investments.
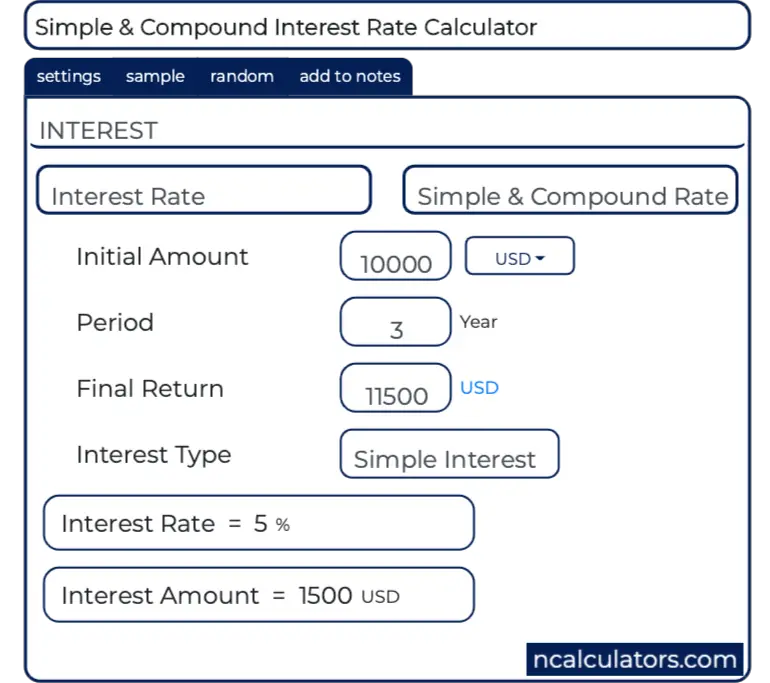
Understanding Interest Rates

When seeking car financing, the interest rate you’ll receive is a critical component affecting your overall payment. Here’s how to better understand it:
- Types of Interest Rates: You’ll encounter fixed rates, which stay constant over the loan term, and variable rates, which can fluctuate based on market conditions.
- Credit Score Impact: Your credit score heavily influences the rate you’ll be offered. Higher scores generally result in lower interest rates.
- Compare Annual Percentage Rates (APRs): APR includes both the interest rate and any additional fees. Comparing APRs can give you a clearer picture of the total cost.

Shop Around for the Best Deals

Different lenders offer different rates based on numerous factors. Here’s how to leverage this to your advantage:
- Get Pre-Approvals: Securing pre-approvals from various lenders can give you a sense of what rates you might qualify for without affecting your credit score too much.
- Negotiate: Remember, rates can often be negotiated. If you have competitive offers, use them as leverage.
- Consider Online Lenders: Online platforms often offer competitive rates due to lower overhead costs.
Understand the Terms of Your Loan

Being aware of the loan terms is as important as the interest rate:
| Loan Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Loan Duration | Longer loan terms might mean lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid. |
| Down Payment | A larger down payment can lower your interest rate and overall loan amount. |
| Early Repayment Options | Some loans penalize you for paying off early; ensure you understand these terms. |
| Dealer Financing vs. Bank Financing | Banks might offer better rates than dealers, but dealers can sometimes provide incentives. |

Consider All Costs

When looking at car finance rates, don’t just focus on the interest rate:
- Fees and Charges: Origination fees, prepayment penalties, and other associated costs can add up.
- Insurance Costs: Some loans require you to carry comprehensive insurance, affecting your monthly budget.
- Depreciation: Know your car’s depreciation rate as it impacts your loan-to-value ratio, possibly affecting rates.
💡 Note: A vehicle with a high residual value might secure better finance rates due to lower risk for the lender.
Negotiate Financing Separately from the Car Price

Here’s how you can maximize your savings:
- Decouple the Negotiations: Finance terms and car purchase price should be negotiated separately for better leverage.
- Use Incentives: If dealers offer incentives tied to financing, consider how these influence your deal.
- Loan Term Flexibility: Sometimes shorter terms can lead to better rates even if the monthly payment is higher.
In summary, navigating car finance rates involves understanding various financial aspects beyond just the interest rate. By comparing rates, terms, and total costs, and by negotiating both the car's price and financing independently, you're well-equipped to secure a deal that's both financially advantageous and meets your budget.
What is the difference between fixed and variable interest rates?

+
Fixed rates remain the same throughout your loan term, providing stability in your payments. Variable rates, however, can change based on market conditions, potentially lowering or increasing your payments over time.
How does my credit score affect my car finance rates?
+
Your credit score significantly impacts the interest rate you’ll receive. Higher scores often qualify for lower rates as you’re seen as less risky by lenders.
Should I choose a shorter or longer loan term?

+
Shorter loan terms might increase your monthly payments but decrease the total interest paid over the life of the loan. Longer terms offer lower monthly payments but more interest over time.