Accounting for Finance Leases: Simplified Guide

When managing the financials of any organization, one critical aspect that often comes into play is how to account for leases. Leases can significantly impact a company's balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statements. Here, we delve into the nuances of Finance Leases, or what were previously known as capital leases under the old accounting rules. Understanding finance leases is paramount for CFOs, financial analysts, and accounting professionals alike. Let's break down what finance leases are and how they should be accounted for in financial statements.
What is a Finance Lease?

A finance lease, under IFRS 16 and ASC 842, is essentially when an asset is transferred from the lessor to the lessee, where the lessee gains most of the economic benefits of the asset and also assumes the risk related to the asset's value. Here's what you need to know:
- Risks and Rewards: The lessee takes on risks associated with ownership, such as obsolescence or damage, along with potential rewards, like increase in value.
- Lease Term: The lease agreement often covers the majority, if not all, of the asset’s economic life.
- Bargain Purchase Option: There might be an option for the lessee to purchase the asset at a price lower than its expected fair value at the end of the lease term.
- Ownership: Although the lessee doesn't legally own the asset, they treat it as such for accounting purposes.
How to Account for Finance Leases?

When a finance lease is entered, here's how it impacts the lessee's financial statements:
Initial Recognition

At the commencement of the lease:
- Recognize a lease liability for the lease payments not yet paid, discounted at the interest rate implicit in the lease, or if that rate is not available, the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate.
- Recognize a right-of-use asset representing the lessee’s right to use the underlying asset over the lease term.
Subsequent Measurement
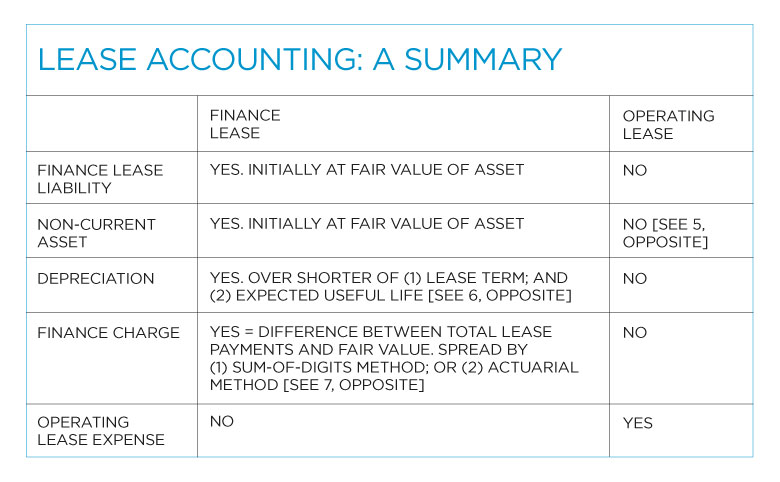
Over the lease term:
- Depreciation: Depreciate the right-of-use asset. If it's reasonably certain to get ownership at the end, depreciate over the asset's useful life. Otherwise, over the shorter of the lease term or useful life.
- Interest Expense: Interest expense is recorded on the lease liability based on the effective interest method. This reflects the unwinding of the discount.
- Lease Payments: Each lease payment reduces the lease liability and is split between the principal and interest. The principal reduces the liability, while the interest is an expense.
Examples of Finance Leases

To illustrate, consider a company leasing machinery with these terms:
| Lease Term | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Annual Lease Payment | $10,000 (due at the beginning of each year) |
| Interest Rate Implicit in the Lease | 6% |
| Fair Value of the Machinery | $40,000 |

💡 Note: This example assumes payments at the start of the year. If payments are due at the end, the calculation would change slightly.
Here's how this lease would be accounted for:
- At commencement:
- Lease liability = Present Value of lease payments ($10,000 for 5 years at 6% annual rate) = $40,000.
- Right-of-use asset = $40,000.
- Over the lease term:
- Depreciation expense would be $8,000 per year ($40,000/5).
- Interest expense would reduce each year as the principal amount decreases.
In the first year:
- Depreciation expense: $8,000
- Lease payment: $10,000 (which includes $2,400 interest ($40,000 x 6%) and $7,600 principal)
- Lease liability reduction: $7,600
- End of Year 1 balance sheet:
- Lease liability: $32,400
- Right-of-use asset (net of depreciation): $32,000
Following years would follow the same pattern, with adjustments for the new liability balance at each payment date.
Understanding finance leases helps companies reflect the true nature of their obligations and assets more transparently on their financial statements. It's important to accurately report these figures for strategic decision-making, investor relations, and compliance with financial regulations.
What is the difference between a finance lease and an operating lease?

+
A finance lease is one where the lessee effectively gains control over the underlying asset, bearing the risks and rewards of ownership. An operating lease, on the other hand, is more like a rental agreement where the lessor retains significant risks and rewards of ownership.
How do changes in lease accounting standards affect businesses?

+
New standards like IFRS 16 and ASC 842 require companies to recognize lease assets and liabilities on the balance sheet, potentially impacting key financial ratios and covenants, as well as increasing transparency in financial reporting.
What happens if a lease isn’t classified correctly?

+
Misclassification can lead to incorrect financial reporting, potentially causing regulatory issues, misinformed investment decisions, or financial misrepresentation, all of which can have significant financial and reputational implications.